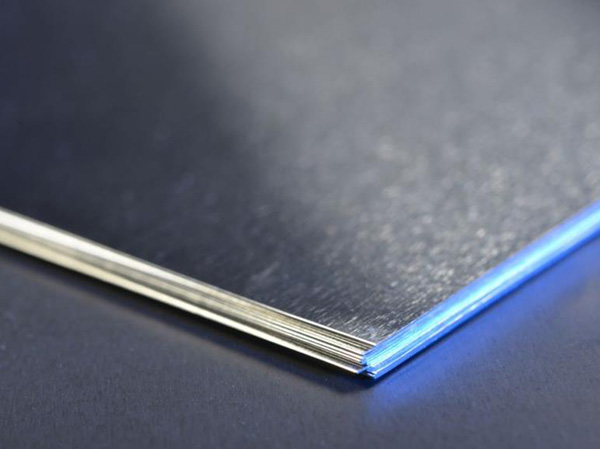
WHAT IS STAINLESS STEEL WELDING TECHNOLOGY?
Stainless steel
welding technology refers to the techniques and methods used to join pieces of
stainless steel through the process of welding. Stainless steel is a
corrosion-resistant alloy that contains iron, chromium, nickel, and other
elements. It is widely used in various industries such as construction,
automotive, aerospace, and more due to its durability, strength, and resistance
to corrosion.
Welding is the
process of joining two or more pieces of metal by melting and fusing them
together. Stainless steel welding requires specialized techniques because of
the unique properties of the material. Some key aspects of stainless steel
welding technology include:
l Material Selection: Choosing the right type of
stainless steel for the specific application is crucial. There are various
grades of stainless steel with different alloy compositions, and each has its
own welding characteristics.
l Welding Methods: Common welding methods for
stainless steel include Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW or TIG), Gas Metal Arc
Welding (GMAW or MIG), and Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW or stick welding).
TIG welding is often preferred for stainless steel due to its precision and
control over the heat input.
l Welding Parameters: Controlling welding parameters
such as current, voltage, travel speed, and shielding gas is essential to
achieve a high-quality weld. Maintaining the right balance helps prevent issues
like overheating or inadequate penetration.
l Joint Preparation: Proper joint preparation is
critical for stainless steel welding. This involves cleaning the surfaces to be
welded, removing any contaminants, and ensuring proper fit-up of the pieces.
l Shielding Gas: In TIG and MIG welding, the use
of appropriate shielding gases, such as argon or a mixture of argon and helium,
is essential to protect the weld from atmospheric contamination and to provide
a stable arc.
l Post-Weld Treatment: Stainless steel welding may
require post-weld treatments, such as pickling and passivation, to remove
oxides and other impurities from the welded area and restore the material's
corrosion resistance.
l Welding Filler Materials: Selecting the right filler
material is crucial for achieving a strong and corrosion-resistant weld.
Matching the filler metal to the base metal's composition is important.

Types Of Stainless Steel Welding
When welding
stainless steel, there are several different methods that can be used. Each
type of welding has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the
intended application.
Ø One common method is TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding, which uses a
non-consumable tungsten electrode to create an electric arc and an inert
shielding gas to protect the weld from contamination. This process produces
clean, precise welds with minimal distortion and excellent control of heat
input.
Ø Another popular option is MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, which uses a
consumable wire and an inert shielding gas fed through a welding gun. MIG
welding is generally faster than TIG, but may produce more spatter and require
more cleanup after completion.
Ø For thicker materials or high-volume production applications, submerged
arc welding (SAW) can be used. SAW involves feeding a continuous wire into the
joint while covering it with flux powder to prevent oxygen and contaminants
from entering.
Ø Other types of stainless steel welding include plasma arc welding,
resistance spot welding, laser beam welding, and electron beam welding. The
choice of technology will depend on factors such as material thickness, desired
finish quality and production volume requirements.