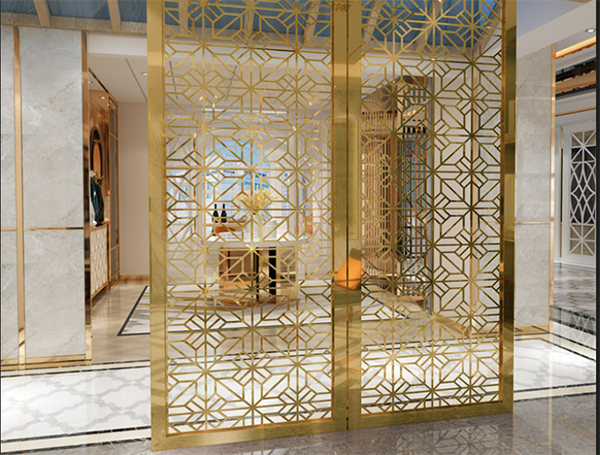
What is PVD Vacuum Coating?
PVD Vacuum coating is performed in a high vacuum environment. It involves heating the evaporation source to evaporation or bombarding and sputtering with ion beams to form a single or multi-layer film on the surface of a substrate (metal, semiconductor or insulator). This technology can be applied in a variety of fields, including but not limited to the production of optical lenses, decorative coatings, material surface modification, and the application of functional films, such as imitation gold plating on watch cases or coating on mechanical tools to improve wear resistance.
In the vacuum coating process, specific targets are usually used as evaporation sources. These targets are rapidly cooled by chiller cooling during the coating process to ensure the stability of the target and precise temperature control of the evaporation source. In addition, chillers are also used to cool vacuum components and the working environment to maintain stable working conditions and prevent excessive temperatures from affecting the coating.
The Difference Between PVD Vacuum Coating and Water Plating
1. Vacuum coating is processed in a vacuum furnace, while water plating is processed in an aqueous solution.
2. The vacuum coating process flow is complex, the environment and equipment requirements are high, and the intermediate coating process involves a transportation process. The water plating process is quite simple. From equipment to environmental requirements, it is not as demanding as vacuum coating, and it can be completed in fully automated production.
3. Vacuum coating now has discontinuous coating that can be non-conductive. The conductivity of products is significantly enhanced after water plating.
4. The color of vacuum coating processing is richer than that of water electroplating, and the color and brightness are brighter than that of water electroplating.
5. The vacuum coating will retain its color for a longer time, will not corrode and oxidize, and its hardness will be slightly worse. The hardness of the water-plated is slightly better, but it is easy to get yellow and corrode.
6. In terms of processing cost, the cost of vacuum coating is higher than that of water plating.
7. Vacuum coating is an environmentally friendly process and the technology is developing rapidly. Water electroplating is a traditional process and is highly polluting.
Will Discoloration Occur at High Temperatures After PVD Coating?
When many users apply the PVD coating process, they are not only pursuing color, but also require the film layer to have certain protective properties for the product as well as the durability and stability of the film layer.
PVD coating is formed by nano-scale particles hitting the target surface at extremely high speeds. After the metal particles hit the surface, they will form a thin film of a few microns to tens of microns, providing protection and decorative effects for the product. But this does not mean that PVD coating is permanent. The coating may undergo some changes if exposed to high temperatures. These changes may include fading in color, spots on the surface, or even peeling of the coating. However, this does not mean that all PVD coatings will undergo these changes.
First of all, different PVD coating materials have different heat resistance. For example, Titanium nitride has very good heat resistance and will not undergo significant color changes even at high temperatures. Some cheaper PVD coating materials, such as chromium oxide, may change at high temperatures. Secondly, even if a coating material with poor heat resistance is used, the heat resistance of the coating can be improved through appropriate surface treatment and coating enhancement technology. For example, color changes and peeling caused by high temperatures can be prevented by adding a protective coating to the coated surface.
High temperatures may have an impact on PVD coatings, but this impact depends on the choice of coating material and the way the surface is treated. Different colors have different film structures, so if you are considering applying PVD coating, especially for parts that require heat resistance.
Which One Has Better Film Density, Water Plating or PVD Coating?
In the surface treatment process, water plating and PVD coating have their own characteristics. Water plating, known for its high density and wear resistance, is widely used in the appearance and protection of various products. PVD coating has attracted much attention for its environmental protection and diversity, and is widely used in high-tech fields. However, in terms of density, PVD coating is slightly better. Its coating structure is tight and almost pore-free, which greatly enhances the hardness and corrosion resistance of the surface. In addition, PVD coating also has the characteristics of strong adhesion, rich colors and environmental protection. In comparison, water plating is slightly less dense, but its advantage is that it is quickly molded and cheap.
Can Vacuum Coating Scratches Be Treated?
First of all, scratches are divided into before and after coating. However, whether before or after coating, fine scratches can be repaired and surface defects removed through fine grinding and polishing technology. But for severe scratches, repair may be more difficult.
What Is The Reason Why Products Rust After Vacuum Coating?
After the products were vacuum coated and subjected to salt spray testing, some did not rust for 72 hours or even longer, and some became rusty after 12 hours. There are also some products that have no problem in the salt spray test, but the products have become rusty during use.
Common reasons for corrosion:
1. Material problems. The base material itself has poor corrosion resistance and can easily cause coated products to rust.
2. The coating quality is poor. The adhesion, density or thickness of the coating layer is insufficient, and it cannot effectively prevent oxygen and moisture from entering the substrate, causing the product to rust.
Common reasons for corrosion during use:
1-The use environment is harsh. Products used in harsh environments such as high temperature, high humidity, and high salt content will accelerate corrosion and rust of the coating.
2- Poor storage environment. Products stored in unfavorable environments, such as coastal areas with high humidity and heavy salt content, or places with severe industrial pollution, can easily lead to corrosion and rust of the coating.
Whether it is a decorative film layer or a functional film layer of vacuum coating, in order to prevent the product from rusting after vacuum coating, it is necessary to use corrosion-resistant high-quality substrates and improve the coating quality. At the same time, attention should be paid to the storage and use environment.