What’s The Stamping
Process For Stainless Steel?
The stamping process for stainless steel involves using a press to shape or cut stainless steel sheets or coils into specific forms or parts. This process is commonly used in the manufacturing of various products such as automotive components, appliances, and aerospace parts.
The stamping process for stainless steel offers high precision and efficiency, making it a cost-effective method for mass production of parts with consistent quality. The specific details of the process may vary depending on the complexity of the part and the requirements of the application.
Stainless steel stamping is to use the stamping process to process stainless steel plates. It is a comprehensive processing technology that integrates cutting, punching, bending, labeling, stretching, molding, twisting and other processes. It is efficient, low-cost, High quality and other advantages.
The
stamping process for stainless steel typically includes the following steps:
l Material
Selection: Choose the appropriate grade of stainless steel based on the
specific requirements of the final product. Common stainless steel grades for
stamping include 201, 304, 316, and 430.
l Sheet
Preparation: The stainless steel is usually provided in the form of sheets or
coils. The material may undergo processes such as leveling, shearing, or
slitting to achieve the desired thickness and dimensions.
l Tool
and Die Design: Design the tooling, including dies and punches, based on the
product's specifications. The tooling will determine the final shape of the
stamped stainless steel part.
l Blanking: In this step, the stainless steel sheet is cut into flat pieces known as blanks.
Precautions
For Stainless Steel Stamping Forming
² Plate
thickness: Stainless steel materials with larger plate thickness are not
suitable for stamping.
² Mold
design: The stress of the material should be concentrated on the parts where
the strain is evenly distributed to avoid excessive stress concentration that
may cause the mold to break or deform.
² Stamping
molding process: Process parameters such as stamping times, speed, and
temperature need to be controlled to ensure molding quality.
² Stamping
center position: The center position should be controlled at the center of the
plate during stamping to avoid stress concentration.
² Plate
surface: The surface of the plate must be protected to prevent scratches and
deformation during the stamping process.
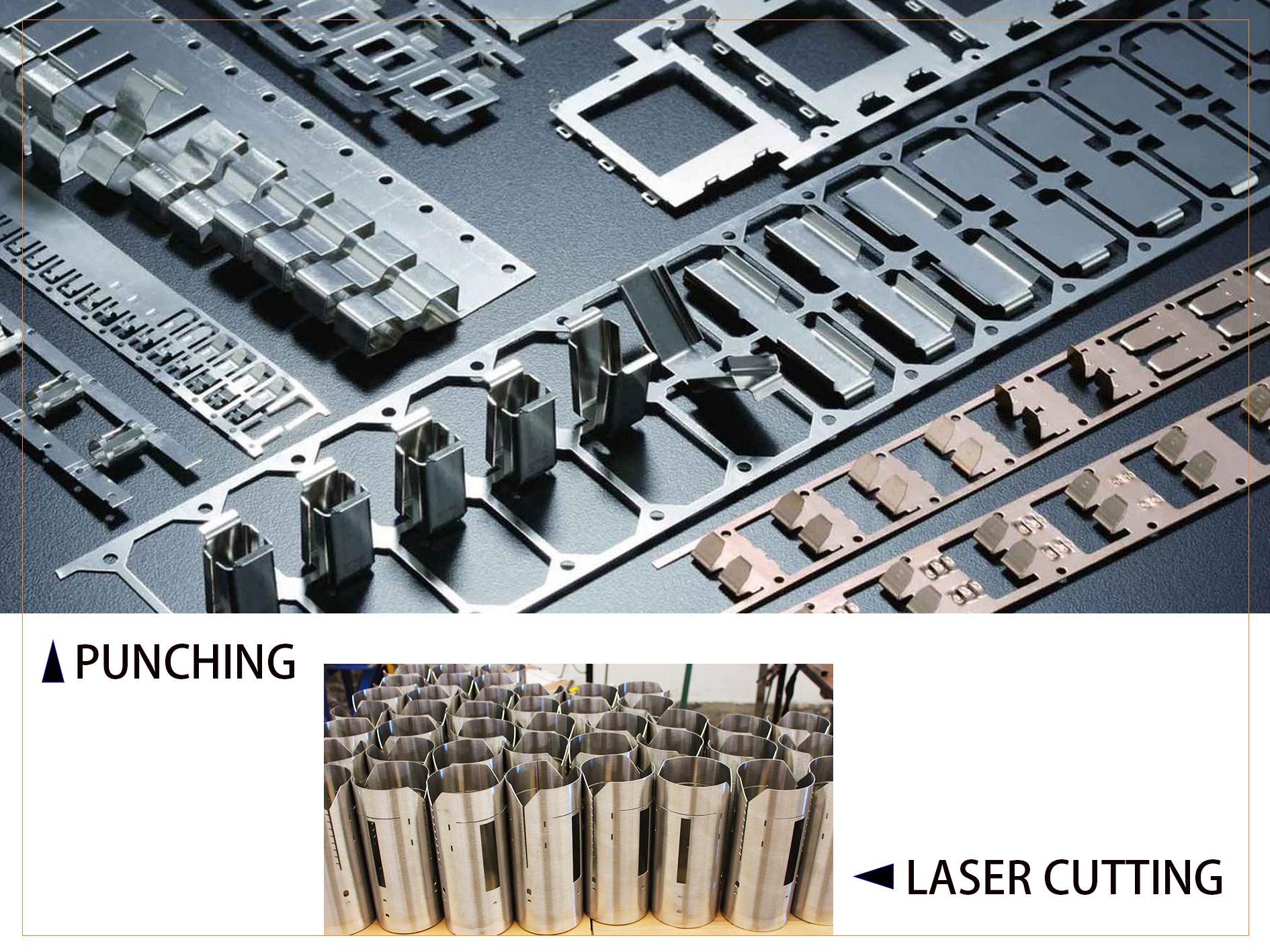
What’s The Difference of The Finish Made By Punching
And Laser Cutting?
Punching
Ø Edge
Quality: The edges of stainless steel parts produced by punching may have a
slight burr or sharp edge. This is because the punching process involves
cutting through the material by applying force with a punch and die, which can
result in some deformation and a raised edge.
Ø Surface Distortion: Punching can cause some distortion on the surface of the material,
particularly around the punched area.
Ø Surface
Finish: The surface finish of punched stainless steel may not be as smooth as
laser-cut stainless steel. However, the finish can still be acceptable for many
applications.
Ø Heat
Affected Zone (HAZ): Punching generates more heat during the process, and this
heat can lead to a heat-affected zone around the cut area. This may affect the
mechanical properties of the material in the vicinity of the cut.
Laser
Cutting
Ø Edge
Quality:
Laser cutting typically provides a high-quality edge with minimal burr. The
precision of laser cutting allows for clean and smooth edges, reducing the need
for additional finishing processes.
Ø Surface Finish: Laser cutting often produces a smoother surface finish compared to punching. The laser beam melts and vaporizes the material, resulting in a more refined and polished appearance.
Ø Tolerance and Precision: Laser cutting is known for its high precision and tight tolerances. This accuracy contributes to a more consistent and refined final product.
Ø Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): Laser cutting produces a narrower heat-affected zone compared to punching, which is advantageous for maintaining material properties.
In summary, while
both punching and laser cutting are viable methods for processing stainless
steel, laser cutting often provides a superior finish in terms of edge quality,
surface finish, and overall precision. However, the choice between the two
methods depends on factors such as the specific application, material
thickness, and production volume, as each method has its advantages and
limitations.